Cruise ships are enormous vessels, practically floating cities. Ships that large require power systems that are more powerful than a speedboat. But what does it take to propel such a large ship?
This guide to cruise ship power systems will explain everything it takes to move cruise ships from port to port worldwide. Cruise ship power systems can vary from ship to ship, but every ship has an engine that uses fuel, usually diesel or gas, sometimes with supplemental electricity.
If you have ever taken a cruise or seen one come into port, you may have wondered what it makes it move. This guide should answer your questions and make it all clearer.
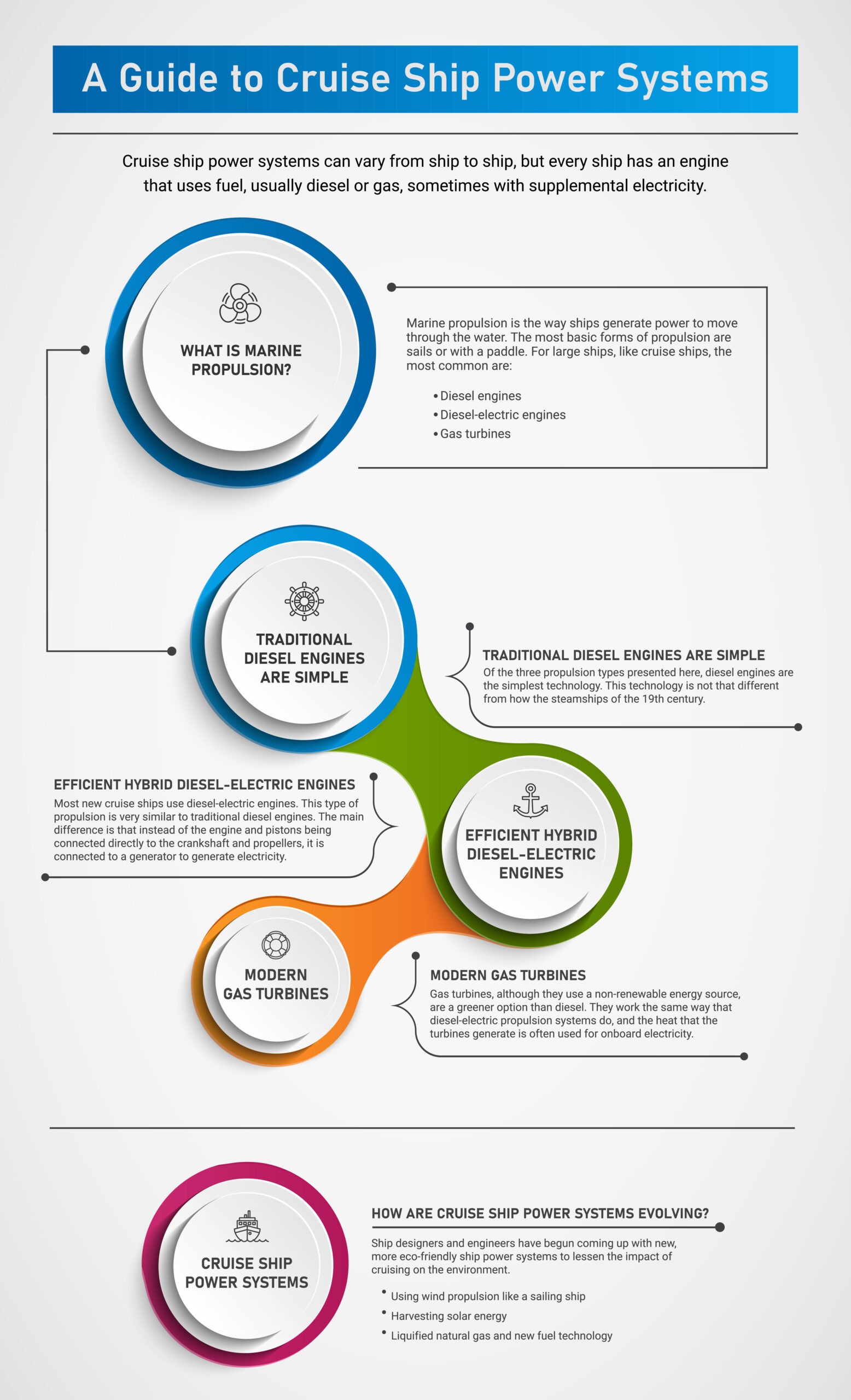
What is Marine Propulsion?
Marine propulsion is the way ships generate power to move through the water. The most basic forms of propulsion are sails or with a paddle. For large ships, like cruise ships, the most common are:
- diesel engines,
- diesel-electric engines
- gas turbines.
Traditional Diesel Engines are Simple
Of the three propulsion types presented here, diesel engines are the simplest technology. This technology is not that different from how the steamships of the 19th century.
Engines use diesel fuel, which, when ignited, drives the engine pistons up and down. The pistons are attached to a crankshaft, and the action of the pistons turns the crankshaft, which is attached to the propeller. The propeller moves the ship through the water at a gentle speed.
Efficient Hybrid Diesel-Electric Engines
Most new cruise ships use diesel-electric engines. This type of propulsion is very similar to traditional diesel engines. The main difference is that instead of the engine and pistons being connected directly to the crankshaft and propellers, it is connected to a generator to generate electricity. This electricity is then used to turn the propellers.
This is a more efficient way of using diesel fuel. Because the pistons are fired by a consistent flow of electricity rather than burning fuel, they move at the most efficient speed. Electricity is also used to pump cool seawater through the engines to cool them and prevent overheating.
The electricity generated from the diesel-electric method can also be used onboard. It is converted to a lower voltage and directed to the cabins for passengers to use.
Modern Gas Turbines New to Cruise Ships
As you can probably imagine, cruise ships require a lot of fuel. Gas turbines, although they use a non-renewable energy source, are a greener option than diesel. They work the same way that diesel-electric propulsion systems do, and the heat that the turbines generate is often used for onboard electricity.
Gas turbines are a relatively new cruise ship power system, but they will probably be used more frequently. Some of the benefits to this engine system are:
- less polluting
- are easier maintenance
- lower chance of fire
- lower noise and vibrations
How Are Engines Stored on a Cruise Ship?
Cruise ship engines are very big and require their own space. The cruise ship engine room is usually located on the lowest deck. Ships designers have historically put the heaviest equipment as low as possible, and nothing is heavier than an engine. Because engines are so big, they can sometimes take up three whole decks.
Rather than having a large room filled with all the different machinery that keeps the ship moving, the engine components are divided up into different rooms. The main engine won’t be in the same room as the air conditioning and heating systems. The main reason for this separation is safety, such as if there is an engine fire.
How Much Fuel Do Cruise Ships Use?
Cruise ships use a lot of fuel. How much is dependent on the size of the ship, the speed it goes, and the distance it travels. The amount of fuel an average cruise ship goes through in a voyage is generally around 300 tons a day.
When ships come into port, they take the opportunity to fill up the fuel tanks. Fueling barges will come up to the ships and load the fuel onboard. When the passengers return from their excursions, the ship is ready to move on.
How Are Cruise Ship Power Systems Evolving?
As the world considers the effects that fossil fuels have on climate change, cruise ships have come under increasing scrutiny. Ship designers and engineers have begun coming up with new, more eco-friendly ship power systems to lessen the impact of cruising on the environment. Although no ships run solely on these power types yet, they supplement fossil fuel systems.
Although fossil fuel powered engines are still widely used in the cruise ship industry, there are already ships implement new technologies. The ones you might see now are:
- Wind power
- Solar power
- Liquefied Natural Gas
Using Wind Propulsion Like a Sailing Ship
When you hear of a wind-powered ship, an old-fashioned sailing ship might be what comes to mind. This is not an image that is compatible with a modern cruise ship. Instead, you should think of modern, electricity generating windmills.
Ships that are equipped to use auxiliary wind power have a special rotor sail on deck that uses the direction of the wind to create a force to keep the ship moving forward. These rotor sails are very sensitive to the wind and can shut down when conditions are unfavorable.
Only a few ships use wind power, but it is a viable option for future ships. Wind power is the traditional method of sailing, and it makes sense to return to it in an effort to be more environmentally conscious.
Harvesting Solar Energy Way of the Future
Solar power is a relatively new form of marine propulsion. It has been used only since the late 2000s but is seeing promise as a more environmentally friendly method of powering cruise ships.
Ships that do use this type of power have usually solar panels affixed to their exteriors. While they are not powerful enough to propel the ship on their own, the electricity generated from these panels is used for supplementary purposes, such as interior lights, elevators, and fuel engines.
In the future, ships might have solar panels shaped like sails. As solar panels become more advanced, they could be capable of powering all of the interior electrical needs. This would cut emissions from fossil fuels drastically.
Liquefied Natural Gas and New Fuel Technology
Though fossil fuel and, therefore, less eco-friendly than wind or solar power, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is a cleaner option than diesel. LNG is 90% methane and 10% ethane, and when it’s cooled to very lower temperatures, it converts from a gas to a liquid. When LNG burns, the emissions released are cleaner than diesel, with no soot or sulfur oxides.
Storage requirements on board for LNG require very large tanks, so this type of fuel is most commonly being used on smaller ships that don’t travel as far, like ferries. But as the technology improves, it should start to be seen on larger cruise ships.
A Cruise Ship Is a Floating City
Cruising is one of the most popular types of tourism today. Ships sail to ports around the world, bringing thousands of people in for the day. It makes sense then that a cruise ship requires powerful propulsion systems to keep them moving.
From coal to solar power, ship designs are always evolving, and engineers are meeting the environmental considerations of the 21st century head-on and planning for a new way of cruising. While some of these power systems seem straight out of a science fiction novel, it’s only a matter of time before they are used everywhere.
Take a look around the next time you are on a cruise ship. Now that you know how cruise ships are powered, you’ll probably see signs of what kind of power systems are propelling your ship. And maybe, before you know it, you’ll be laying on the deck below solar panel sails.






